Lawyer
New member
- Joined
- Jul 2, 2020
- Messages
- 7
- Reputation
- 13
Introduction
Eye prominence plays a very important role on how your face is perceived, deep-set eyes are a male dimorphic trait, it has been hypothesized that deep-set eyes may be an adaptation for combat, hunting and male intrasexual selection, designed to protect the eyes from hits.
As you can see in the following image, towards the more masculine faces, the eyes become vertically narrower and more sunken:

Eye prominence is determined by the projection of the orbital rims in relation to the cornea.
The relationship of the globe to the orbital rims is a primary determinant of the appearance of the upper third of the face. Normal values are shown in the following image:

Classification of eye prominence
To measure the degree of eye prominence a hertel exophthalmometer is used, this device measures the position of the globe in relation to the lateral orbital rim.
The normal range of ocular protrusion as measured from the lateral orbital rim to the corneal apex is 14–21 mm in adults.
Depending on your exophthalmometry measurement, your eyes will be:
Orbital vector
Eye prominence can also be measured with the orbital vector, the orbital vector is determined by the linear relationship of the most anterior projection of the globe to the most anterior projection of the lower eyelid and the malar eminence.
According to this relationship, the orbital vector will be:
Negative and positive orbital vectors:

The malar eminence is the most prominent point of the zygomatic bone (malar bone) and is always located anterior to the infraorbital rim, this is something that should be taken into account when augmenting the infraorbital rims with implants.
In most cases, a positive vector equates to a deep-set eye, while a negative vector results in a prominent eye.
Achieving deep-set eyes
To achieve deep-set eyes, you can either reduce the prominence of the globe or increase the projection of the orbital rims, in some cases both approaches may be necessary to achieve deep-set eyes.
The surgical procedure to reduce the promience of the eyeballs is called orbital decompression, it involves removing or thinning various safe orbital walls (and orbital fat), thereby expanding the eye socket, allowing the eyeball to settle back.
The best and safest first orbital wall to remove (or thin out) is the lateral orbital wall, followed by the medial wall, and last the orbital floor. More reduction with added risk is taken as more walls are decompressed. Incisions are hidden in the lateral upper eyelid crease (for lateral orbital decompression), caruncle or transcaruncular (for medial wall decompression) and lower eyelid conjunctiva (for orbital floor decompression).
Before and after pics of bilateral orbital decompression:

To increase the projection of the orbital rims you can get orbital implants.
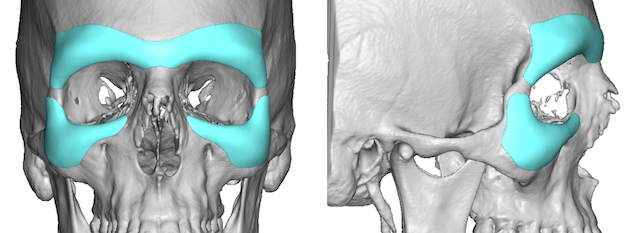
Also some osteotomies can augment the orbital rims:
LeFort 3 and Modified LeFort 3 advance the infraorbital and lateral orbital rims.
LeFort 3:

Modified LeFort 3:


Quadrangular LeFort 2 advances the infraorbital rims

Eye prominence plays a very important role on how your face is perceived, deep-set eyes are a male dimorphic trait, it has been hypothesized that deep-set eyes may be an adaptation for combat, hunting and male intrasexual selection, designed to protect the eyes from hits.
Under the influence of high estrogen levels, a young woman gains about 35 pounds of fat, changing the shape of her breasts, hips, thighs and lips. By contrast, a young man acquires about one and half times as much muscle and bone mass, controlled by the complex action of androgens (and aromatized androgens) acting both directly and indirectly (via release of growth hormone) on bone and muscle tissues. As a result, the average adult male has a longer and broader lower jaw than that of a female, and brow ridge growth results in more sunken narrow eyes.
Even masculine facial structure may be designed for fighting; heavy brow ridges protect eyes from blows, and robust mandibles lessen the risk of catastrophic jaw fractures, for example.
As you can see in the following image, towards the more masculine faces, the eyes become vertically narrower and more sunken:
Eye prominence is determined by the projection of the orbital rims in relation to the cornea.
On average, the surface of the soft tissues overlying the supraorbital rim lies 10 mm anterior to the cornea, and the surface of the soft tissues overlying the infraorbital rim lies 3 mm behind the anterior surface of the cornea. This implies that the supraorbital rim usually projects 13 mm beyond the infraorbital rim.
When the orbital rims have a greater projection beyond the anterior surface of the cornea, the eyes appear "deep set", when the orbital rims project less, the eyes appear "prominent".
The relationship of the globe to the orbital rims is a primary determinant of the appearance of the upper third of the face. Normal values are shown in the following image:
Classification of eye prominence
To measure the degree of eye prominence a hertel exophthalmometer is used, this device measures the position of the globe in relation to the lateral orbital rim.
The normal range of ocular protrusion as measured from the lateral orbital rim to the corneal apex is 14–21 mm in adults.
Depending on your exophthalmometry measurement, your eyes will be:
-Deep-set (<14mm)
-Normal (15 to 17mm)
-Moderately prominent (18 to 20mm)
-Very prominent (>20mm)
Orbital vector
Eye prominence can also be measured with the orbital vector, the orbital vector is determined by the linear relationship of the most anterior projection of the globe to the most anterior projection of the lower eyelid and the malar eminence.
According to this relationship, the orbital vector will be:
-Positive vector: The most anterior portion of the globe lies posterior to the lower eyelid margin, which lies posterior to the anterior malar eminence.
-Neutral vector: The anterior globe, lower eyelid margin, and anterior malar eminence all lie in the same vertical plane.
-Negative vector: The anterior globe lies anterior to the lower eyelid margin, which lies anterior to the malar eminence.
Negative and positive orbital vectors:
The malar eminence is the most prominent point of the zygomatic bone (malar bone) and is always located anterior to the infraorbital rim, this is something that should be taken into account when augmenting the infraorbital rims with implants.
In most cases, a positive vector equates to a deep-set eye, while a negative vector results in a prominent eye.
Achieving deep-set eyes
To achieve deep-set eyes, you can either reduce the prominence of the globe or increase the projection of the orbital rims, in some cases both approaches may be necessary to achieve deep-set eyes.
The surgical procedure to reduce the promience of the eyeballs is called orbital decompression, it involves removing or thinning various safe orbital walls (and orbital fat), thereby expanding the eye socket, allowing the eyeball to settle back.
The best and safest first orbital wall to remove (or thin out) is the lateral orbital wall, followed by the medial wall, and last the orbital floor. More reduction with added risk is taken as more walls are decompressed. Incisions are hidden in the lateral upper eyelid crease (for lateral orbital decompression), caruncle or transcaruncular (for medial wall decompression) and lower eyelid conjunctiva (for orbital floor decompression).
Before and after pics of bilateral orbital decompression:
To increase the projection of the orbital rims you can get orbital implants.

Plastic Surgery Case Study - Combined Custom Brow Bone and Infraorbital Implants for Periorbital Augmentation for Prominent Eyes - Explore Plastic Surgery
Custom periorbital implants consist of superior brow bone implants and infraornital rim implants that come close or meet over the lateral orbital rims.
exploreplasticsurgery.com
Also some osteotomies can augment the orbital rims:
LeFort 3 and Modified LeFort 3 advance the infraorbital and lateral orbital rims.
LeFort 3:
Modified LeFort 3:
Quadrangular LeFort 2 advances the infraorbital rims
