Lawyer
New member
- Joined
- Jul 2, 2020
- Messages
- 7
- Reputation
- 13
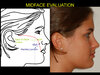
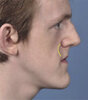
To assess maxillary deficiency and paranasal flatness, we must observe the cheekbone-nasal base-lip contour (CP-Nb-LC)
The cheekbone-nasal base-lip contour is determined by the cheekbone point (CP) and the maxilla point (MxP).
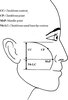
The cheekbone point, in a subject with good facial proportions, is the most prominent point of the cheekbone that is located 20–25 mm inferior and 5–10 mm anterior to the outer canthus of the eye when viewed in profile and is 20–25 mm inferior and 5–10 mm lateral to the outer canthus of the eye when viewed frontally.
The maxilla point is the most anterior point of the cheekbone-nasal base-lip contour, it is an indicator of maxillary anteroposterior position.

Ideally, the cheekbone-nasal base-lip contour should be convex, smooth and uninterrupted and the MxP should be located directly behind the alar base.
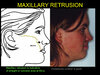
Paranasal flatness is present when there's a straight or concave contour at the MxP.

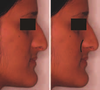
Another useful indicator of midface deficiency is the ratio of the linear distance from the nasal tip to subnasale and from subnasale to the alar base crease. The ratio should be 2:1
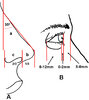
The cheekbone-nasal base-lip contour is determined by the cheekbone point (CP) and the maxilla point (MxP).
The cheekbone point, in a subject with good facial proportions, is the most prominent point of the cheekbone that is located 20–25 mm inferior and 5–10 mm anterior to the outer canthus of the eye when viewed in profile and is 20–25 mm inferior and 5–10 mm lateral to the outer canthus of the eye when viewed frontally.
The maxilla point is the most anterior point of the cheekbone-nasal base-lip contour, it is an indicator of maxillary anteroposterior position.
Ideally, the cheekbone-nasal base-lip contour should be convex, smooth and uninterrupted and the MxP should be located directly behind the alar base.

Paranasal flatness is present when there's a straight or concave contour at the MxP.


Another useful indicator of midface deficiency is the ratio of the linear distance from the nasal tip to subnasale and from subnasale to the alar base crease. The ratio should be 2:1

A ratio closer to 1:1 will indicate paranasal flatness, whereas an increased ratio will indicate decreased nasal projection.(A) The nasal projection can further be evaluated by measuring the angle between the nasal dorsum and a vertical line. The angle should be 34 degrees for females and 36 degrees for males. (a) The relationship between the nasal tip–columella (b) and lobule–ala (c) of 1:2 is helpful to distinguish between paranasal flattening (maxillary anteroposterior deficiency) or overprojection of the nasal tip.