Choosing the best procedure to augment the chin: Is anything better than an implant?
ucdavis.pure.elsevier.com
There are four basic options possible to augment the chin:
- Surgical placement of an alloplast implant.
- Bony osteotomy with advancement of the chin (sliding genioplasty).
- Augmentation with injectable fillers.
- Augmentation with autologous fat.
IMPLANTS
Augmentation of the chin with an implant is a simple procedure that provides excellent augmentation of the bony pogonion. It is thus a good choice for horizontal microgenia in patients with good chin symmetry and normal vertical chin height (►Fig. 1A–D).
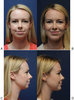
Fig. 1 Preoperative (A) frontal and (C) lateral photographs of a 32-year-old patient with horizontal microgenia. (B, D) Three months postoperative photographs of the patient after augmentation with a Silastic chin implant.
Microgenia - Wikipedia
Implants are generally not good for patients with vertical chin deficiency or excess, or in patients with any significant asymmetry of the chin.
Chin convexity should also be taken into account when choosing the implant size:

Estimating chin implant size based on chin convexity
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3792756/ Conventionally, the ideal chin is thought to be one that is 1mm to 3mm posterior to a vertical plane dropped from the vermilion border of the lower lip in the profile view (Figure1A). A chin that doesn't meet this requirement is considered...
 forum.looksmaxxing.com
forum.looksmaxxing.com
This technique is also limited by the availability of various sizes and shapes of alloplast implants. An infinite number of shapes and sizes of implants may be required. However, most implants are manufactured in only three or four sizes and one or two shapes, in most of the cases custom designed implants are needed to achieve an optimal result.
GENIOPLASTY
Osteotomy of the bony mentum (osseous genioplasty) is a versatile and reliable procedure for correcting a variety of skeletal chin deformities. This technique involves horizontal osteotomy and downfracture of the chin, with repositioning and fixation of the distal segment. Correction of both horizontal and vertical chin deficiencies can be performed.
Additionally, if transverse issues exist, such as transverse asymmetry or narrowness of the chin, improvement can be gained to better the overall chin shape.
Widening Genioplasty - Plastic Surgeon | Dr. Barry L. Eppley, MD
A widening genioplasty bring the chin bone and widens it as well through a midline bony cut and interpositional bone graft.
 www.eppleyplasticsurgery.com
www.eppleyplasticsurgery.com
INJECTABLE FILLERS AND AUTOLOGOUS FAT
Augmentation of the chin can also be accomplished with injection of soft-tissue fillers or autologous fat. Despite the fact that these techniques are not permanent, they have the advantages of not requiring incisions and not resulting in scarring.
Injectable fillers or autologous fat augmentation also allows correction of the chin in three dimensions. As such, injectable procedures are ideal for modifying chin shape (►Fig. 4A–F).
Fig. 4 (A–C) Preinjection photographs of a middle-aged male patient with a deep labiomental sulcus, horizontal microgenia, and a narrow chin shape. (D–F) Postinjection photographs of the same patient after injection with 2-mL JUVÉDERM Ultra Plus (1 mL centrally deep to the mentalis muscle and 0.5 mL to each lateral mandibular region; Allergan, Irvine, CA).
DECIDING ON THE MOST SUITABLE CHIN AUGMENTATION PROCEDURE
A factor that impacts decision making in chin augmentation is practitioner bias. This bias is affected by training and experience. Surgeons tend to choose the procedure with which they have had the most experience. Facial plastic surgeons have been exposed to and have learned to augment chins by surgical placement of an alloplast implant. Oral surgeons have more experience with sliding bony genioplasty. Most dermatologists do not perform surgical chin enhancement; therefore, they tend to recommend fillers for chin augmentation.
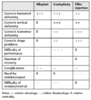
The ideal chin augmentation procedure would be effective, adjustable, predictable, and safe. ►Table 1 lists the relative advantages and disadvantages of each chin augmentation procedure. No technique is ideal, each one has certain advantages.
Surgical enhancement procedures, including chin augmentation with an alloplast and bony chin osteotomies, have the advantage of being permanent solutions, thereby obviating the need for additional treatment (should the surgical result be satisfying to the patient and safe). However, surgery on the chin produces a permanent change. If the patient is not satisfied with the surgical result or if postsurgical complications arise, additional surgery may be required.
A second surgical procedure after implant placement requires implant removal or adjustment, while postsurgical issues after chin osteotomies require a second surgery and osteotomy to change chin contour.
Injection of autologous fat or injectable fillers is a relatively simple procedure that can occur under topical anesthesia (if filler is injected) or under local anesthesia (with or without sedation) with autologous fat transfer. These procedures have the advantage of allowing chin augmentation without surgical scarring. These techniques do not require protracted postoperative healing and have the advantage of being predictable and adjustable.
An additional advantage of injectable filling to augment the chin is that filling with a needle or canula allows 3D chin “shaping.” Augmentation with an alloplast limits the practitioner in that a finite array of implant sizes and shapes exist and the variations of underlying chin contours are vast.