- Joined
- Jul 15, 2025
- Messages
- 4,139
- Time Online
- 12d 20h
- Reputation
- 14,896
this thread will be educating u n*****s on how to properly grow biiig muscles, no MICROTEAR bullshit
SPLITS
INTENSITY > VOLUME
Excessive volume only fatigues your muscles, causing you to perform poorly and limits your intensity in each set.
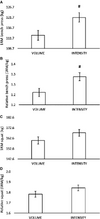
This graph shows a significant difference in relative and 1RM bench press strength over 6 weeks, indicating that a high intensity, low volume split stimulates significantly greater 1RM bench press and lean arm gains compared to a high volume, moderate intensity split.
HIGH FREQUENCY > LOW FREQUENCY
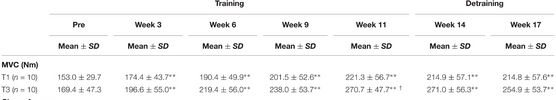
T1 = 1x FREQUENCY T3 = 3x FREQUENCY
This study outlines the difference in MVC (maximum voluntary contraction) between each group, peaking at a 26.1% difference in Week 11
Although this may seem insignificant, this study failed to maintain a control group as well as not determining the nutritional status for each group, which can be a huge limiting factor in overall muscle growth. However, it demonstrates my point: high frequency > low frequency
With this information, the best splits for optimal muscle growth appear to be:
FULL BODY EVERY OTHER DAY (FBEOD)
To program a FBEOD split, I recommend training each muscle for 1-2 sets, within the 4-6 rep range.
1 set allows you to achieve a high intensity, low volume workout without the compromise of fatigue.
FBEOD is high frequency, with you training each muscle group 3-4x a week.
UPPER LOWER (ULULRR, ULR)
To program an upper lower split, 2 sets within the 6-8 rep range is ideal.
ULULRR = Upper, Lower, Upper, Lower, Rest, Rest
ULR = Upper, Lower, Rest
Either variation guarantees a 2x frequency per week for each muscle group.
MECHANICAL TENSION
MECHANICAL TENSION IS THE MAIN DRIVE FOR MUSCLE GROWTH.
Mechanical tension is the physical force placed on your muscles through resistance training, which then signal your mechanoreceptors to build more muscle tissue = HYPERTROPHY
MICROTEARS are microscopic injuries to the muscle fibres, once thought to be the main cause of muscle growth. They are simply a secondary factor which may contribute to adaptation and remodelling, but are useless to hypertrophy.
REP RANGES
A 4-8 rep range (varies depending on your split) is important to optimise mechanical tension, as the heavy resistance requires your nervous system to recruit a high number of motor units, therefore leading to more mechanical tension, which is crucial for hypertrophy.
TRAINING TO FAILURE is the most important factor in the recruitment of motor units, as demonstrated in this graph.
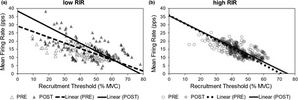
low RIR = 0-1 reps from failure
high RIR = 4-6 reps from failure
NUTRITION AND REST
This should be common sense, but 2-3 rest days within your split and approximately 8-10 hours of sleep is critical for muscle growth.
For nutrition, 1.6-2.2 grams of protein per kg of body weight is optimal for building muscle.
Personally, I would recommend you stay away from soy protein, whey protein, etc, and focus on getting your protein intake from mainly meat, dairy and eggs.
However, this is not mandatory for recovery.
Anyway goys I hope this helps
@dipenhydramine
SPLITS
INTENSITY > VOLUME
Excessive volume only fatigues your muscles, causing you to perform poorly and limits your intensity in each set.

This graph shows a significant difference in relative and 1RM bench press strength over 6 weeks, indicating that a high intensity, low volume split stimulates significantly greater 1RM bench press and lean arm gains compared to a high volume, moderate intensity split.
HIGH FREQUENCY > LOW FREQUENCY

T1 = 1x FREQUENCY T3 = 3x FREQUENCY
This study outlines the difference in MVC (maximum voluntary contraction) between each group, peaking at a 26.1% difference in Week 11
Although this may seem insignificant, this study failed to maintain a control group as well as not determining the nutritional status for each group, which can be a huge limiting factor in overall muscle growth. However, it demonstrates my point: high frequency > low frequency
With this information, the best splits for optimal muscle growth appear to be:
FULL BODY EVERY OTHER DAY (FBEOD)
To program a FBEOD split, I recommend training each muscle for 1-2 sets, within the 4-6 rep range.
1 set allows you to achieve a high intensity, low volume workout without the compromise of fatigue.
FBEOD is high frequency, with you training each muscle group 3-4x a week.
UPPER LOWER (ULULRR, ULR)
To program an upper lower split, 2 sets within the 6-8 rep range is ideal.
ULULRR = Upper, Lower, Upper, Lower, Rest, Rest
ULR = Upper, Lower, Rest
Either variation guarantees a 2x frequency per week for each muscle group.
MECHANICAL TENSION
MECHANICAL TENSION IS THE MAIN DRIVE FOR MUSCLE GROWTH.
Mechanical tension is the physical force placed on your muscles through resistance training, which then signal your mechanoreceptors to build more muscle tissue = HYPERTROPHY
MICROTEARS are microscopic injuries to the muscle fibres, once thought to be the main cause of muscle growth. They are simply a secondary factor which may contribute to adaptation and remodelling, but are useless to hypertrophy.
REP RANGES
A 4-8 rep range (varies depending on your split) is important to optimise mechanical tension, as the heavy resistance requires your nervous system to recruit a high number of motor units, therefore leading to more mechanical tension, which is crucial for hypertrophy.
TRAINING TO FAILURE is the most important factor in the recruitment of motor units, as demonstrated in this graph.

low RIR = 0-1 reps from failure
high RIR = 4-6 reps from failure
NUTRITION AND REST
This should be common sense, but 2-3 rest days within your split and approximately 8-10 hours of sleep is critical for muscle growth.
For nutrition, 1.6-2.2 grams of protein per kg of body weight is optimal for building muscle.
Personally, I would recommend you stay away from soy protein, whey protein, etc, and focus on getting your protein intake from mainly meat, dairy and eggs.
However, this is not mandatory for recovery.
Anyway goys I hope this helps
@dipenhydramine