- Joined
- Sep 22, 2023
- Messages
- 7,929
- Time Online
- 7d 12h
- Reputation
- 21,007
- Location
- Ancient Carthage
- Guild
- Order of Nihil
Trimaxillary osteotomy, is a surgical procedure used to correct severe jaw misalignment or deformities, such as overbites, underbites, or crossbites. This procedure involves repositioning both the upper jaw (maxilla) and the lower jaw (mandible) to improve alignment and function.
During the surgery, the surgeon makes precise cuts in the upper and lower jaws to allow them to be moved into the correct position. In some cases, additional procedures may be performed to address other facial structures, such as the chin or cheekbones.
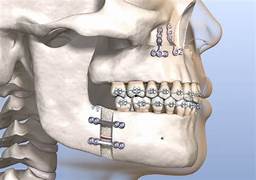 Trimaxillary osteotomy is typically performed by oral and maxillofacial surgeons in collaboration with orthodontists. Before surgery, patients usually undergo orthodontic treatment to align the teeth as much as possible. After the surgery, further orthodontic adjustments may be needed to fine-tune the bite.
Trimaxillary osteotomy is typically performed by oral and maxillofacial surgeons in collaboration with orthodontists. Before surgery, patients usually undergo orthodontic treatment to align the teeth as much as possible. After the surgery, further orthodontic adjustments may be needed to fine-tune the bite.
The goals of trimaxillary osteotomy include improving facial aesthetics, restoring proper function of the jaws for chewing and speaking, and alleviating any associated breathing problems. This procedure is often considered for individuals with severe jaw discrepancies that cannot be corrected with orthodontics alone.

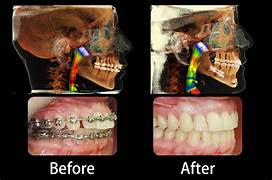
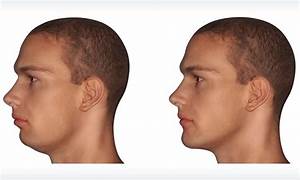
During the surgery, the surgeon makes precise cuts in the upper and lower jaws to allow them to be moved into the correct position. In some cases, additional procedures may be performed to address other facial structures, such as the chin or cheekbones.
The goals of trimaxillary osteotomy include improving facial aesthetics, restoring proper function of the jaws for chewing and speaking, and alleviating any associated breathing problems. This procedure is often considered for individuals with severe jaw discrepancies that cannot be corrected with orthodontics alone.